Teeth Wearing
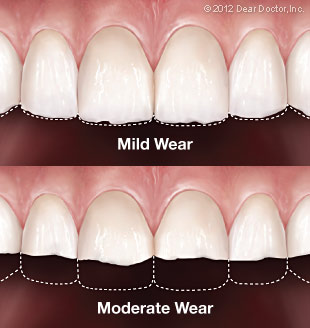 Tooth wear is the term used to describe the progressive loss of a tooth’s surface due to actions other than those which cause tooth decay or dental trauma.
Tooth wear is the term used to describe the progressive loss of a tooth’s surface due to actions other than those which cause tooth decay or dental trauma.
Prevalence of tooth wears increases with age.
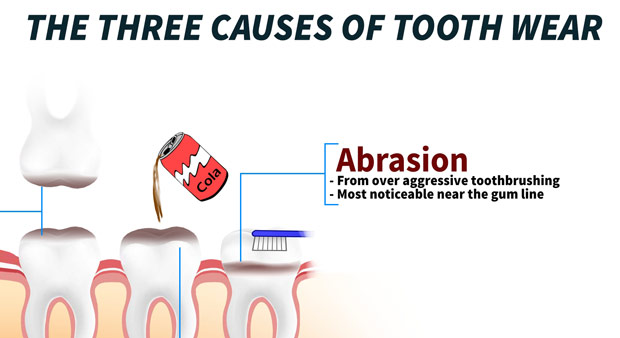 Tooth wear is caused by three phenomena: Erosion, Attrition and Abrasion.
Tooth wear is caused by three phenomena: Erosion, Attrition and Abrasion.
Erosion is loss of tooth substance by chemical or acid dissolution, and no bacteria are involved. Erosion of tooth surfaces is mostly the results of too frequent or inappropriate use of carbonated drinks and fruit juices with high levels of acidity,erosion is also seen in individuals with gastro oesophageal reflux disease (GERD )
Attrition is the progressive loss of hard tooth substances caused by chewing or grinding between opposing teeth.Increase in people who habitually clench or grind their teeth (a condition known as bruxism), e.g., during sleep.
Abrasion is the progressive loss of hard tooth substances caused by mechanical actions other than mastication. Abrasion is commonly associated with incorrect tooth brushing technique, giving rise to notching at the junction of the crown and root of teeth. It will also be seen in individuals who use their teeth as a tool (e.g., to remove bottle tops, to hold pins, clips or nails).
 ✓ Sensitivity in chewing surface or flat front tooth edges.
✓ Sensitivity in chewing surface or flat front tooth edges.
✓ Pain the tooth
✓ Notching on tooth surface with or without sensitivity at the junction of teeth and gums
 Erosion
Erosion
Dietary counseling involving less acidic foods and drinks
Selecting medicines with minimal effects on teeth
Attrition
If tooth loss is minimal selective grinding is done to effect physiological jaw movement .
If more tooth loss is present ,restoration or root canal treatment with crown are done to effect physiological jaw movement.
Soft bite guards are given to treat habitual night grinding and protect teeth from wearing.
Abrasion
If abrasion is shallow ,the edges are only smoothened and fluorides are applied .
If sensitivity is present ,restorations are done.
If abrasions are deep root canal treatment with crown or tooth removal may be necessary.
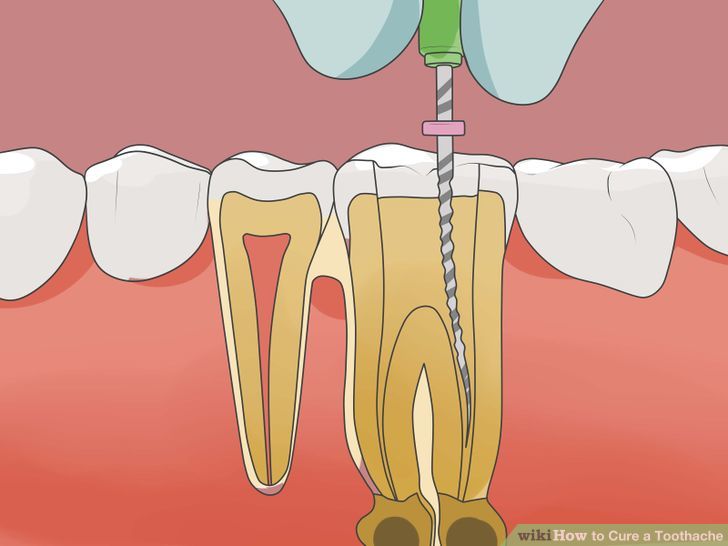
If any tooth wear process is allowed to continue, the destruction can reach the center of the tooth, the pulp. The longer the actions causing the damage continue, the more work will be needed to correct the problem.
 Reducing the frequency of drinking carbonated drinks and fruit juices with high levels of acidity is the key to preventing erosion of the teeth.
Reducing the frequency of drinking carbonated drinks and fruit juices with high levels of acidity is the key to preventing erosion of the teeth.
Toothbrushing should be avoided immediately after consuming acidic drinks and foods for a period of time (at least 20 minutes), as the acid softens the enamel making it susceptible to damage from brushing.
Attrition is a slow-progressing condition and many people will only be made aware of the damage to their teeth on visiting the dentist.
In the case of bruxism, treatment may require the wearing of a bite guard during sleep.
Abrasion can be reduced by adopting a correct toothbrushing technique . In particular, the soft toothbrush should be held using a pen-grip and vigorous horizontal scrubbing actions with a hard toothbrush should be avoided.
Toothpastes vary in their level of abrasiveness.Fluoride toothpastes also help to combat tooth wear, specifically erosive tooth wear, as the availability of fluoride promotes the formation of a calcium flouride layer.
