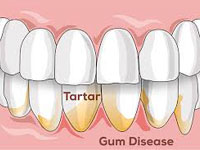
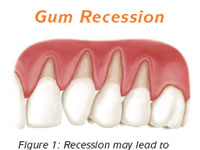
Receding gums
 Receding gums is the exposure in the roots of the teeth caused by a loss of gum tissue or retraction of gum
tissue from the tooth. Gum recession is a common dental problem. Most people don't know they have gum recession
because it occurs gradually. There are treatments that can repair the gum and prevent further damage.
Receding gums is the exposure in the roots of the teeth caused by a loss of gum tissue or retraction of gum
tissue from the tooth. Gum recession is a common dental problem. Most people don't know they have gum recession
because it occurs gradually. There are treatments that can repair the gum and prevent further damage.
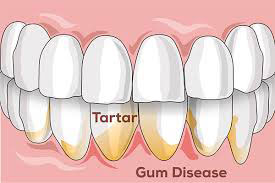 Pain at the gum line,
Pain at the gum line,
Visibly shrinking gums,
Tooth sensitivity,
Exposed tooth roots
(tooth appear longer than normal).
 Pocket depth reduction Surgery
Pocket depth reduction Surgery
If inflammation and deep pockets remain following treatment with deep cleaning ,your dentist will decide
whether you will need surgery. Pocket reduction surgery is a deep tissue cleaning where your dentist lifts
back the gums, removes the tartar and then puts them back in place with sutures.
Bone or tissue grafting
In grafting, the goal is to resuscitate either gum tissues or the bones. In this procedure tissue regeneration
is done by inserting a small piece of mesh-like fabric is inserted between the bone and gum tissue to allow the
regrowth of bone. A gum graft can reduce further recession and bone loss. It can cover exposed roots to protect
them from decay and tooth sensitivity. It’s important to note that this process cannot be successful over the
long term without proper oral health care.
 Brushing twice a day to reduce plaque build up.
Choose a soft bristled tooth brush and use moderate pressure
Consider a night guard – clenching of teeth can cause gums to recede.
Regular dental visits for early identification and treatment
Brushing twice a day to reduce plaque build up.
Choose a soft bristled tooth brush and use moderate pressure
Consider a night guard – clenching of teeth can cause gums to recede.
Regular dental visits for early identification and treatment